Nobel Laureate Lecture
My Journey of Discovery Lecture Series
David J. Wineland
Nobel Laureate in Physics

David J. Wineland
Nobel Laureate in Physics
David Jeffrey Wineland (born February 24, 1944, in Wauwatosa, Wisconsin) is an American physicist celebrated for his pioneering research in quantum mechanics and atomic physics. He was awarded the 2012 Nobel Prize in Physics, which he shared with French physicist Serge Haroche, for their groundbreaking work on observing and controlling individual quantum systems, especially trapped ions. Wineland’s work has been instrumental in advancing the fields of quantum information processing, quantum optics, and precise timekeeping. His work has not only redefined precision timekeeping but also has profound implications for fundamental physics and applications such as GPS technology, navigation, and synchronization in communication systems.
Landmark Contributions
of Wineland’s in areas of Physics

Laser Cooling of Ions
David Wineland, together with Hans Georg Dehmelt, was one of the pioneers in the development of Doppler cooling, a technique that uses laser light to reduce the motion of ions or atoms, bringing them to near absolute zero. This method was simultaneously…
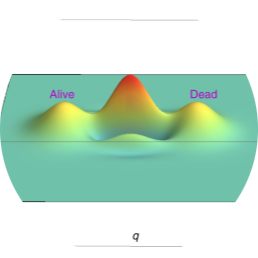
Schrödinger’s Cat
David Wineland’s pioneering research on isolating and controlling individual ions has played a central role in advancing quantum mechanics and quantum information science. By conducting experiments in a vacuum to minimize external interference…

Quantum Computing
David Wineland’s team made a groundbreaking contribution to quantum computing by demonstrating the first-ever quantum logic gateoperation using two isolated quantum bits (qubits). This experiment, published in 1995, was a significant step toward…

Atomic Clocks and Precision Measurement
David Wineland’s pioneering work in atomic clocks has resulted in the development of optical clocks that are over ten times more accurate than traditional cesium-based atomic clocks…

Resolved Side band Cooling
Resolved sideband cooling is a laser cooling technique that allows atoms and ions to be cooled beyond the limits of traditional methods, such as Doppler cooling, by reaching their lowest possible energy state, or zero-point energy. This technique is crucial…
David's Key Papers
Published influential Scientific Papers
Quantum Dynamics of Single Trapped Ions
Single trapped ions represent elementary quantum systems that are well isolated from the environment. They can be brought nearly to rest by laser cooling, and both their internal electronic states and external motion can be coupled to and manipulated by light fields…
Demonstration of a Fundamental Quantum Logic Gate
Demonstrate the operation of a two-bit” controlled-NOT” quantum logic gate, which, in conjunction with simple single-bit operations, forms a universal quantum logic gate for quantum computation. The two quantum bits are stored in the internal and external…

A “Schrödinger cat” superposition state of an atom
A “Schrödinger cat”-like state of matter was generated at the single atom level. A trapped 9Be+ ion was laser-cooled to the zero-point energy and then prepared in a superposition of spatially separated coherent harmonic oscillator states. This state was created by application…

Quantum Zeno Effect
The quantum Zero effect is the inhibition of transitions between quantum states by frequent measurements of the state. The inhibition arises because the measurement causes a collapse (reduction) of the wave function. If the time between measurements is short enough, the wave function usually collapses…

Experimental violation of a Bell's inequality with efficient detection
Local realism is the idea that objects have definite properties whether or not they are measured, and that measurements of these properties are not affected by events taking place sufficiently far away. Einstein, Podolsky and Rosen used these…
Awards & Honors
Wineland's received numerous prestigious awards

2019
Micius Quantum Prize

2012
Nobel Prize in Physics
shared with Serge Haroche

2010
Benjamin Franklin Medal in Physics

2007
National Medal of Science

2001
Arthur L. Schawlow Prize in Laser Science
Featured Video
Nobel Laureate Lecture
" If we succeed in building a quantum computer, we would be able to solve problems that are beyond the capability of classical computers, no matter how fast they become. "
David J. Wineland
Nobel Laureate in Physics
Related Lectures and Conferences
Knowledge Partners
IIT Hyderabad

IIT Tirupati

School of Humanities, Social Sciences
and Management,
IIT Bhubaneswar

Sanskriti
University

SOA University

Sister Nivedita University

Government P.G. College
Ranikhet
Jijñāsā Group
IIT Bhubaneswar

Dr. T. D. Singh’s Quest Club
IISc Bangalore

Amity University
Gurugram
For Queries
Contact
lecture@binstitute.org
+91 93815 64100
+91 75698 65357
+91 93815 64100
+91 75698 65357








