Meldal's
Landmark Contributions
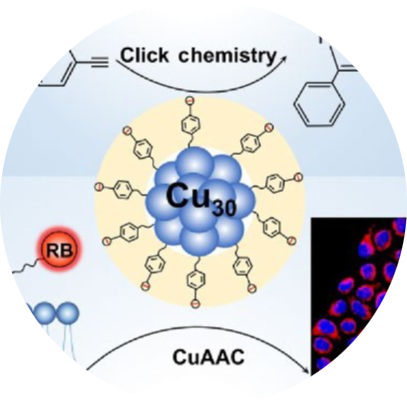
Click Chemistry and CuAAC Reaction
Click Chemistry is a concept introduced by K. Barry Sharpless in 2001, referring to highly efficient, selective, and reliable chemical reactions that “click” molecules together like puzzle pieces. These reactions are simple, fast, high-yielding, and work in mild conditions, making them ideal for drug development, biomolecular labeling, and materials science.
One of the most important reactions in click chemistry is the Copper-Catalyzed Azide-Alkyne Cycloaddition (CuAAC), independently discovered by Morten P. Meldal and K. Barry Sharpless.
This reaction involves:
- An azide (-N₃) and an alkyne (-C≡C) reacting in the presence of a copper(I) catalyst.
- The reaction forms a stable 1,2,3-triazole ring, a structure useful in medicinal chemistry, bioorthogonal chemistry, and polymer science.
- CuAAC is highly selective, efficient, and bio-compatible, making it widely used in drug discovery, nanotechnology, and chemical biology.
Prof. Morten P. Meldal’s contribution to CuAAC made it a gold standard reaction in modern chemistry, leading to his 2022 Nobel Prize in Chemistry.
Solid-Phase and Combinatorial Chemistry
Solid-Phase Chemistry is a method where molecules are synthesized while attached to a solid support (such as resin beads). This technique allows for easy purification, as excess reagents and byproducts can be washed away without complicated separation steps. It was first developed for peptide synthesis by Robert Bruce Merrifield and later expanded by researchers like Morten P. Meldal to other organic molecules, including carbohydrates and small-molecule drugs.
Combinatorial Chemistry is a powerful technique that enables the rapid synthesis of large libraries of compounds by systematically combining different building blocks.
By using solid-phase synthesis, chemists can create thousands or millions of unique molecules at once, which can then be screened for drug discovery, materials science, and biochemical applications.
Prof. Morten P. Meldal made significant contributions to solid-phase and combinatorial chemistry, particularly in peptide and drug discovery, by developing efficient methods for synthesizing and screening new bioactive molecules. His work has greatly accelerated the search for new pharmaceuticals and functional materials.
Peptide and Carbohydrate Chemistry
Peptide Chemistry focuses on the synthesis, structure, and function of peptides, which are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Peptides play crucial roles in biological processes, drug development, and biomaterials. Advances in solid-phase peptide synthesis (SPPS), pioneered by Morten P. Meldal and others, have made it easier to produce peptides for medicinal and biochemical research. Peptides are widely used in hormones, antibiotics, and cancer therapies.
Carbohydrate Chemistry involves the study of sugars (monosaccharides) and their polymers (polysaccharides), which are essential in cell signaling, energy storage, and immune responses.
The synthesis of complex carbohydrates is challenging due to their structural diversity, but solid-phase and click chemistry methods have improved their production. Meldal contributed to automated carbohydrate synthesis, making it easier to study glycoproteins, vaccines, and sugar-based therapeutics.
His work in peptide and carbohydrate chemistry has led to advancements in drug design, biomolecular engineering, and medical diagnostics.
Catalysis and Reaction Development
Catalysis is the process of using a catalyst to speed up a chemical reaction without being consumed in the process. Catalysts are crucial in organic synthesis, drug development, and industrial chemistry, as they improve efficiency, selectivity, and sustainability.
Reaction Development focuses on designing new chemical reactions that are more efficient, selective, and environmentally friendly. This includes optimizing conditions, discovering new catalytic systems, and improving reaction mechanisms.
Prof. Morten P. Meldal has contributed to catalysis by developing copper-catalyzed reactions, particularly the Copper-Catalyzed Azide-Alkyne Cycloaddition (CuAAC), which is a key part of click chemistry. His work has led to mild, bio-compatible, and highly selective reactions widely used in drug synthesis, materials science, and chemical biology.
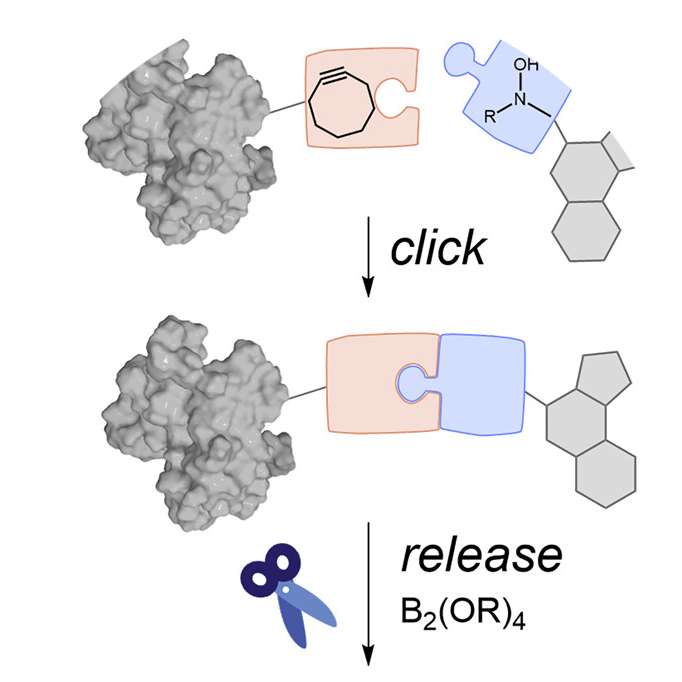
Chemical Biology and Bioconjugation
Chemical Biology is an interdisciplinary field that applies chemical techniques to study and manipulate biological systems. It focuses on designing small molecules, probes, and reactions to understand cellular functions, protein interactions, and disease mechanisms.
Bioconjugation refers to chemically linking biomolecules (such as proteins, peptides, DNA, or drugs) to other molecules like fluorescent tags, nanoparticles, or therapeutic agents. This is essential for drug delivery, imaging, and diagnostics.
Prof. Morten P. Meldal played a major role in advancing bioconjugation techniques, particularly through click chemistry. His CuAAC reaction allows for highly selective and efficient attachment of biomolecules, enabling breakthroughs in drug targeting, bioimaging, and nanomedicine.
